Assessment of Soil Degradation and Resilience Index across Different Topographic Positions in Wukari, Taraba State, Nigeria
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.70110/osse.v3i1.26Keywords:
Land Management, Organic Matter Depletion, PCA, Resilience Index, Soil Degradation, Topographic Positions, WukariAbstract
ackground: Soil degradation is a major challenge to agricultural productivity, particularly in continuously cultivated landscapes.
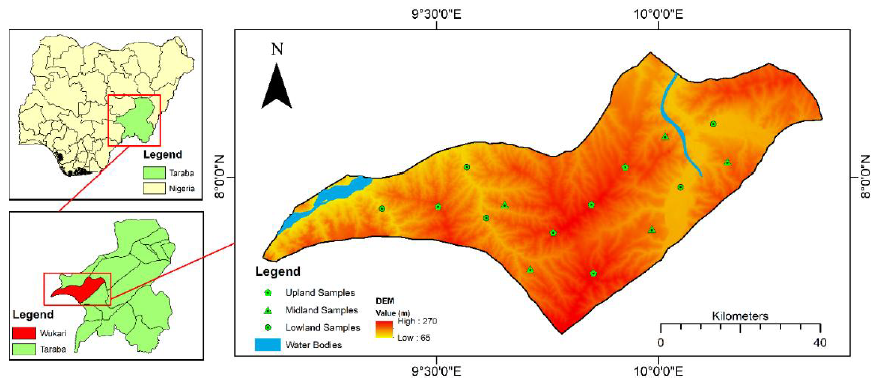
Aims: This study assesses soil degradation and resilience across upland, midland, and lowland topographic positions in Wukari, Taraba State, Nigeria, using Principal Component Analysis (PCA), Hierarchical Cluster Analysis (HCA), and weighted index assessments.
Methods: A stratified random sampling approach was employed to collect 15 composite soil samples, which were analyzed for physical, chemical, and biological indicators of degradation.
Result: Results revealed that organic matter depletion was the most severe degradation factor across all terrain positions, with the upland exhibiting the highest level of degradation. Soil permeability was also significantly degraded in the upland, likely due to higher sand content and lower microporosity. Nitrogen depletion and elevated Exchangeable Sodium Percentage (ESP) were observed across all positions, indicating widespread fertility decline. The weighted degradation index (WDI) classified all positions as moderately degraded, with the upland (WDI = 2.35) experiencing the highest degradation, followed by the midland (1.8) and lowland (1.75). The resilience index (ISR) indicated that upland soils had low resilience (ISR = 0.30), whereas midland and lowland soils were moderately resilient (0.36). To mitigate degradation, organic matter restoration, conservation tillage, and erosion control are recommended for uplands, while controlled irrigation and balanced fertilization should be prioritized for midland and lowland soils. Further research should explore long-term soil monitoring to assess the effectiveness of these strategies.
Downloads
References
Awe, G. O., Nurudeen, O. O., Ogunleye, K. S., & Ayodele, A. A. (2021). Geo-multivariate analysis of crop yield and soil properties of students industrial training farm in Ado Ekiti, Southwest Nigeria. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 67(7), 903-918. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2020.1767773
Awwal A. Y., Maniyunda L. M., & Sadiq F. K. (2022). Distribution and Characteristics of Soils along a Toposequence in Northern Guinea Savanna of Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Soil and Environmental Research, 21, 110 – 121.
Awwal Y.A. & Maniyunda L.M. (2023). Toposequence effect on soil properties and suitability rating for selected crops in Northern Guinea Savanna, Nigeria. Journal of Agriculture and Environment. 19 (2), 215-235.
Awwal, A.Y., Onokebhagbe, V.O., & Adegboye K.A. 2020, Degradation assessment of fallowed and cultivated soils of Teaching and Research Farm, Federal University Dutse, Jigawa State. Proceedings of the 44th Conference of SSSN “Coal City”. Colloquia SSSN 44 (2020), 67-70.
Awwal, Y.A. (2021). Influence of toposequence on soil properties, genesis, suitability and degradation at Hayin Gada, Zaria Nigeria. MSc. Thesis. Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria.
Basak B.B., Sarkar B., Saha A., Sarkar A., Mandal S., Biswas J.K., Wang K., & Bolan N.S. (2022). Revamping highly weathered soils in the tropics with biochar application: What we know and what is needed. Science of the Total Environment, 822, 153461, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153461.
Blanco-Canqui, H. & Lal, R. (2010) Principles of Soil Conservation and Management. Springer.
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8709-7.
Carroll L.N., Au A.P., Detwiler L.T., Fu T., Painter I.S., Abernethy N.F. (2014). Visualization and analytics tools for infectious disease epidemiology: A systematic review. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 51, 287–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2014.04.006
Gee, G.W., Or, D., 2002. Particle-size analysis. In: Dane, J.H., Topp, G.C. (Eds.), Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 4. Physical Methods. SSSA, Inc., Madison, WI, pp. 255-294.
GLASOD, (1998). Global assessment of soil degradation. Guidlines for General Assessment of the status of Human-induced soil Degradation. Wageingen (Netherlands) ISRIC and UNEP.
Havlin J.L. (2005). Fertility. In: Hillel D. (2005). Encyclopedia of Soils in the Environment, Elsevier, 2005, 10-19, https://doi.org/10.1016/B0-12-348530-4/00228-9.
Ibrahim M.M. & Idoga S. (2013). Soil Degradation Assessment of the University of Agriculture Makurdi Students Industrial Work Experience Scheme (SIWES) Farm, Makurdi, Benue State. PAT NSUK Journal, 9 (2): 126-135.
Jakšić, S., Ninkov, J., Milić, S., Vasin, J., Živanov, M., Perović, V., Banjac, B., Vučković, S., Dozet, G., & Komlen, V. (2021). Topographic Position, Land Use and Soil Management Effects on Soil Organic Carbon (Vineyard Region of Niš, Serbia). Agronomy, 11(7), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11071438.
Jimoh A.I., Akande D., Agaku T. D., Haruna S. and Mbaya L. A. (2017). Impact of Toposequence on Soil Properties and Classification in Zaria, Kaduna State, Northern Guinea Savanna, Nigeria. Oral Presentation at Association of Nigerian Geographers 2017 Conference. Retrieved 1/10/2019 at 09:19 am via https://www.researchgate.com.
Jimoh, I.A. (2015). Characterization and Suitability Evaluation of Kubanni Floodplain and Adjoining Upland Soils for Maize and Rice Production in Zaria, Nigeria. MSc. Research. Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria. 87 pp.
Klute, A. (1986). Methods of soil analysis. Part 1: Physical and mineralogical methods. 2nd Ed. America Society Agronomy and Soil Science Society of America Madison, WI
Lal, R. (2003) Soil Erosion and the Global Carbon Budget. Environmental International, 29, 437-450.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00192-7
Lal, R. (2015) Sustainable Intensification for Adaptation and Mitigation of Climate Change and Advancement of Food Security in Africa. In: Lal, R., Singh, B.R., Mwaseba, D.L., Kraybill, D., Hansen, D.O. and Eik, L.O., Eds., Sustainable Intensification to Advance Food Security and Enhance Climate Resilience in Africa, Chapter 1, Springer, Berlin, 3-17.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09360-4_1
Lardy J.M., DeSutter T.M., Daigh A.L.M., Meehan M.A., Staricka J.A. (2022). Effects of soil bulk density and water content on penetration resistance. Agricultural and Environmental Letters, 7(2) 2022, e20096. https://doi.org/10.1002/ael2.20096
Maniyunda L.M. (2012). Pedogenesis of a Lithosequence in the Northern Guinea Savanna of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Ph.D Desertation. Ahmadu Bello University Zaria, Nigeria.
Maniyunda, L.M., Awwal, Y.A. and Daudu, C.K. (2020). Land Degradation Assessment Along a Toposequence in Hayin Gada, Sub Humid Agroecological Zone, Kaduna State Nigeria. Nigerian Journal of Soil and Environmental Research. 19, 61 - 70
Olaniyi A.O., Abioye W.A. (2023). Comparative assessment of soil degradation potentials of commodity crops grown in Nigeria. Agricultura Tropica Et Subtropica, 56 OV, 19–32. https://doi.org/10.2478/ats-2023-0003.
Onoyima, C. C., & Okibe, F. G. (2021). Multivariate analysis of the physico-chemical properties of soils in selected locations of the floodplain of river Kaduna in Niger state, Nigeria. Global Journal of Pure and Applied Sciences, 27(3). 279-288.
Pacheco, F.A.L.; Fernandes, L.F.S.; Junior, R.F.V.; Valera, C.A.; & Pissarra, T.C.T. (2018). Land degradation: Multiple environmental consequences and routes to neutrality. Current Opinion in Environmental Science & Health, 5, 79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coesh.2018.07.002
Qadir, M., & Oster, J. (2004). Crop and irrigation management strategies for saline- sodic soils and watersaimed at environmentally sustainable agriculture. Science of The Total Environment, 323, 1–19.
Reuters. (2024, September 25). Debate rages over push for new green revolution in Africa's agriculture. Reuters. https://www.reuters.com/sustainability/land-use-biodiversity/debate-rages-over-push-new-green-revolution-africas-agriculture-2024-09-25/
Schwilch G., Bestelmeyer B, Bunning S., Critchley W., Herrick J., Kellner K., Liniger H.P., Nachtergaele F., Ritsema C.J., Schuster B., Tabo R., van Lynden G., Winslow M. (2011). Experiences in Monitoring and Assessment of Sustainable Land Management. Land Degradation & Development, 22 (2), 214-225. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.1040
Senjobi, B.A. & Ogunkunle, A.O. (2011). Effect of different land use types and their implications on land degradation and productivity in Ogun State, Nigeria. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology and Sustainable Development, 3(1), 7-18.
Six, J., R. T. Conant, E. A. Paul, & K. Paustian. 2002. Stabilization mechanisms of soil organic matter: Implications for C-saturation of soils. Plant and Soil, 241, 155-176. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016125726789
Tsui C., Chen Z, & Hsieh C. (2004). Relationships between soil properties and slope position in a lowland rain forest of southern Taiwan. Geoderma, 123 (1–2), 131-142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2004.01.031
Upadhyay S., & Raghubanshi A.S. (2020). Chapter 16 - Determinants of soil carbon dynamics in urban ecosystems. In: Verma P., Singh P., Singh R., Raghubanshi A.S. (2020). Urban Ecology, Elsevier, 299-314. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-820730-7.00016-1.
Uyovbisere, E.O., Ogunwole J.O., Ogunwole, J.O., Odigie, V.O., Abdu, N. (2013). Laboratory manual of routine soil, water, plant and fertilizer analyses. A compilation of the Department of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture, Ahmadu Bello University, Zaria, Nigeria.
Weil R.R., and Brady N.C. (2017). The Nature and Properties of Soils. 15th Edition. Pearson Education Publisher. ISBN: 978-0133254488
Yang, M., Zhou, D., Hang, H., Chen, S., Liu, H., Su, J., Lv, H., Jia, H., & Zhao, G. (2024). Effects of Balancing Exchangeable Cations Ca, Mg, and K on the Growth of Tomato Seedlings (Solanum lycopersicum L.) Based on Increased Soil Cation Exchange Capacity. Agronomy, 14(3), 629. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030629
Zuni A. and Jaiyeoba, I. A. (2015). An Assessment of Soil Degradation in Zaria Area, Kaduna State, Nigeria. Ife Research Publications in Geography 13 (2015) 26 – 36.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Adashu Tanko Gani, Yasin Agono Awwal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.









